GENEVA, June 18 (UNHCR)—Wars, conflict and persecution have forced more people than at any other time since records began to flee their homes and seek refuge and safety elsewhere, according to a new report from the UN refugee agency.
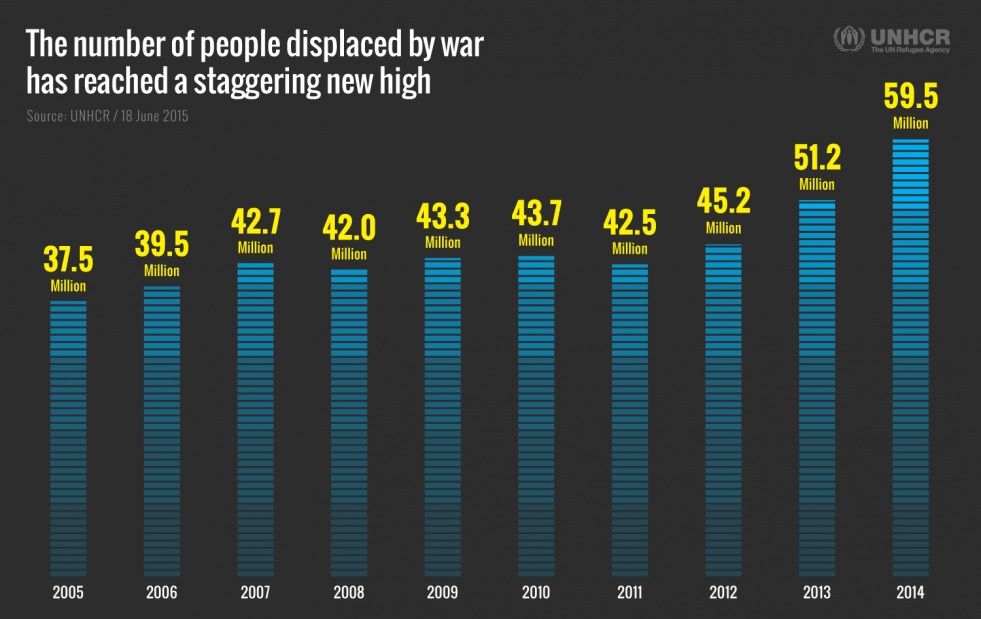
UNHCR’s annual Global Trends Report: World at War, released on Thursday (June 18), said that worldwide displacement was at the highest level ever recorded. It said the number of people forcibly displaced at the end of 2014 had risen to a staggering 59.5 million compared to 51.2 million a year earlier and 37.5 million a decade ago.
The increase represents the biggest leap ever seen in a single year. Moreover, the report said the situation was likely to worsen still further.
Globally, one in every 122 humans is now either a refugee, internally displaced, or seeking asylum. If this were the population of a country, it would be the world’s 24th biggest.
“We are witnessing a paradigm change, an unchecked slide into an era in which the scale of global forced displacement as well as the response required is now clearly dwarfing anything seen before,” said UN High Commissioner for Refugees António Guterres.
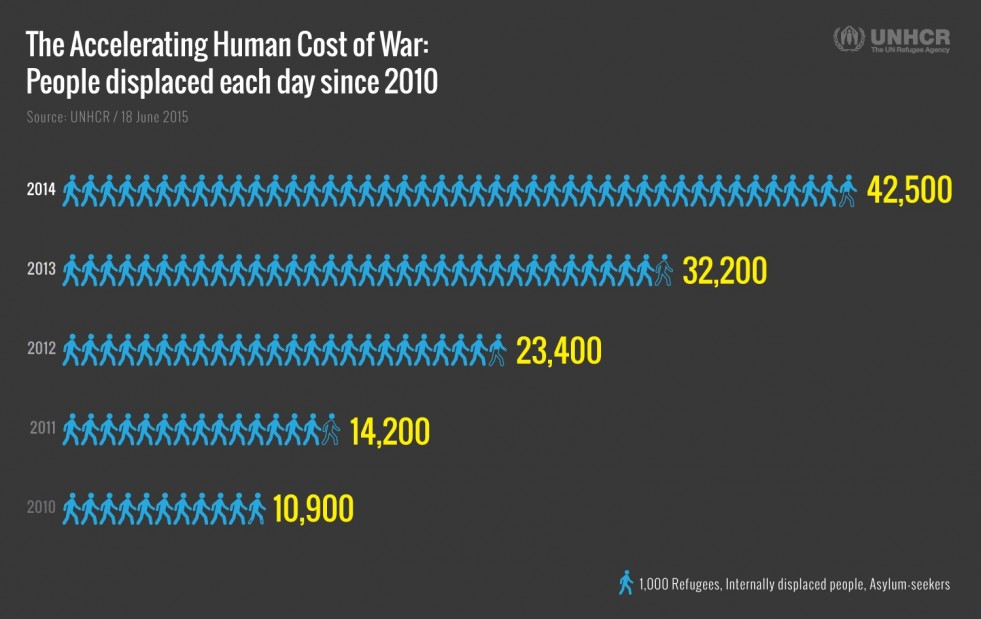
Since early 2011, the main reason for the acceleration has been the war in Syria, now the world’s single-largest driver of displacement. Every day last year on average 42,500 people became refugees, asylum seekers, or internally displaced, a four-fold increase in just four years.
“It is terrifying that on the one hand there is more and more impunity for those starting conflicts, and on the other there is seeming utter inability of the international community to work together to stop wars and build and preserve peace,” Guterres added.
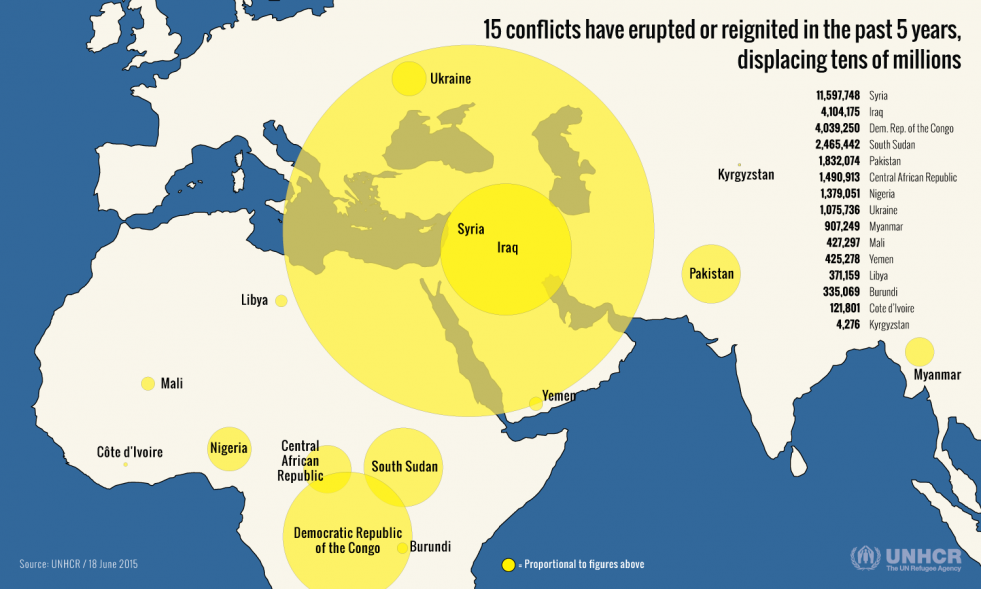
The UNHCR report detailed how in region after region, the number of refugees and internally displaced people is on the rise. In the past five years, at least 15 conflicts have erupted or reignited: eight in Africa (Côte d’Ivoire, Central African Republic, Libya, Mali, northeastern Nigeria, Democratic Republic of Congo, South Sudan and this year in Burundi); three in the Middle East (Syria, Iraq, and Yemen); one in Europe (Ukraine) and three in Asia (Kyrgyzstan, and in several areas of Myanmar and Pakistan).
“Few of these crises have been resolved and most still generate new displacement,” the report noted, adding that in 2014 only 126,800 refugees were able to return to their home countries — the lowest number in 31 years.
Meanwhile, decades-old instability and conflict in Afghanistan, Somalia and elsewhere means that millions of people remain on the move or – as is increasingly common – stranded for years on the edge of society as long-term internally displaced or refugees.
One of the most recent and highly visible consequences of the world’s conflicts and the terrible suffering they cause has been the dramatic growth in the numbers of refugees seeking safety through dangerous sea journeys, including on the Mediterranean, in the Gulf of Aden and Red Sea, and in Southeast Asia.
Half of all refugees are children
The Global Trends report detailed that in 2014 alone 13.9 million people became newly displaced – four times the number of the previous year. Worldwide there were 19.5 million refugees (up from 16.7 million in 2013), 38.2 million were displaced inside their own countries (up from 33.3 million in 2013), and 1.8 million people were awaiting the outcome of claims for asylum (against 1.2 million in 2013).
Most alarmingly, however, it showed that over half the world’s refugees are children.
“With huge shortages of funding and wide gaps in the global regime for protecting victims of war, people in need of compassion, aid and refuge are being abandoned,” warned Guterres. “For an age of unprecedented mass displacement, we need an unprecedented humanitarian response and a renewed global commitment to tolerance and protection for people fleeing conflict and persecution.”
Syria is the world’s biggest producer of both internally displaced people (7.6 million) and refugees (3.88 million at the end of 2014). Afghanistan (2.59 million) and Somalia (1.1 million) are the next biggest refugee source countries.
Almost nine out of every 10 refugees (86 per cent) are in regions and countries considered economically less developed.
Europe (up 51%)
Conflict in Ukraine, a record 219,000 Mediterranean crossings, and the large number of Syrian refugees in Turkey – which in 2014 became the world’s top refugee-hosting nation with 1.59 million Syrian refugees at year’s end – brought increased public attention, both positive and negative, to questions to do with refugees.
In the EU, the biggest volume of asylum applications was in Germany and Sweden. Overall, forced displacement numbers in Europe totalled 6.7 million at the end of the year, compared to 4.4 million at the end of 2013, and with the largest proportion of this being Syrians in Turkey and Ukrainians in the Russian Federation.
Middle East and North Africa (up 19%)
Syria’s ongoing war, with 7.6 million people displaced internally, and 3.88 million people displaced into the surrounding region and beyond as refugees, has alone made the Middle East the world’s largest producer and host of forced displacement. Adding to the high totals from Syria was a new displacement of least 2.6 million people in Iraq and 309,000 newly displaced in Libya.
Sub-Saharan Africa (Up 17%)
Africa’s numerous conflicts, including in Central African Republic, South Sudan, Somalia, Nigeria, Democratic Republic of Congo and elsewhere, together produced immense forced displacement totals in 2014, on a scale only marginally lower than in the Middle East.
In all, sub-Saharan Africa saw 3.7 million refugees and 11.4 million internally displaced people, 4.5 million of whom were newly displaced in 2014. The 17 per cent overall increase excludes Nigeria, as methodology for counting internal displacement changed during 2014 and it could not be reliably calculated. Ethiopia replaced Kenya as the largest refugee-hosting country in Africa and the fifth largest worldwide.
Asia (up 31%)
Long one of the world’s major displacement producing regions, the number of refugees and internally displaced people in Asia grew by 31 per cent in 2014 to 9 million people. Continuing displacement was also seen in and from Myanmar in 2014, including of Rohingya from Rakhine state and in the Kachin and Northern Shan regions. Iran and Pakistan remained two of the world’s top four refugee hosting countries.
Americas (up 12%)
The Americas also saw a rise in forced displacement. The number of Colombian refugees dropped by 36,300 to 360,300 over the year, although mainly because of a revision in the numbers of refugees reported by Venezuela. Colombia continued, nonetheless to have one of the world’s largest internally displaced populations, reported at 6 million people and with 137,000 Colombians being newly displaced during the year. With more people fleeing gang violence or other forms of persecution in Central America, the United States saw 36,800 more asylum claims than in 2013, representing growth of 44 per cent.
The full Global Trends report with this information and more, and including data on individual countries, demographics, numbers of people returning to their countries, and available estimates of stateless population is available at UNCHR.org.